BASIC COMPONENTS OF A BUILDING - BUILDING MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION (StudyCivilEngg.com)
BASIC COMPONENTS OF A BUILDING
SUBJECT : BUILDING MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION
BASIC COMPONENTS OF A BUILDING
The basic components of a building are as follows
- Foundation
- Plinth
- Walls and columns
- Sills, lintels and chajjas
- Doors, windows and ventilators
- Floors
- Roofs
- Steps, stairs, lifts and ramps
- Finishing work
- Building services
Foundation
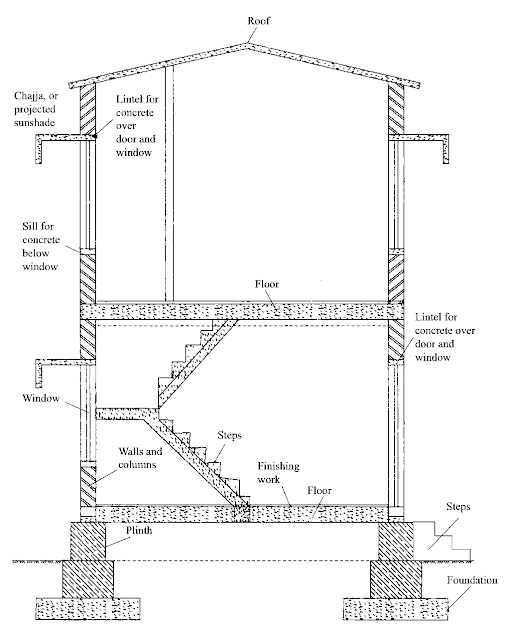
The foundation is the lowermost load-bearing part of the building. Building activity starts with digging the ground for the foundation and then building on it. A foundation serves the following purposes
- It distributes the load evenly and safely from the structure to the soil
- It anchors the building firmly to the ground so that the building does not move under any lateral load
- It prevents the overturning of the building due to lateral forces
- It provides a level surface for the construction of superstructure
Plinth
The portion of the building between the ground level and the ground floor level is called plinth. It is usually of stone masonry. If the foundation is on piles, a plinth beam is cast to support the superstructure. A damp-proof course is provided at the top of the plinth. It is usually a 75 mm thick plain concrete course. The function of the plinth is to keep the ground floor above ground level so that the floor is free from dampness. Its height, which is not less than 450 mm, is governed by the requirement that it is at least 150 mm above the road level, so that connection to underground drainages can be made.
Walls and Columns
Walls and columns are components of buildings that transfer the loads vertically downward. The loads from the roof and floors are transferred to the foundation. Apart from this, the main functions of walls are as given below
- They divide building area into different compartments and provide privacy
- They provide safety from burglars and insects
- They keep the building warm in winter and cool in summer
Sills, Lintels and Chajjas
Windows should not be placed directly over walls. They are placed over a plain concrete course of 50–75 mm thickness provided over the masonry. This course, known as sill, provides a good wearing surface and also an excellent level surface to place window frames.
Lintels are RCC or stone beams provided over door and window openings for transferring load transversely so that the door and window frames are not unduly stressed. They may be continuous or of cut size. The width of lintels is equal to that of walls, while the thickness depends on the width of the opening.
A chajja is a projection given outside the wall to protect doors and windows from rain and sunlight. Usually, it is made of RCC, but in low-cost houses, stone slabs may be provided as chajjas. The chajja projection varies from 600–800 mm. Sometimes, drops are provided to chajjas to improve the aesthetic appearance and also give additional protection from the sun and rain.
Doors, Windows and Ventilators
The function of a door is to give access to different rooms in the building and deny access whenever necessary. The number of doors should be the minimum possible. The size should be such as to facilitate the movement of the largest object likely to pass through the door.
Windows are provided in the exterior walls to provide light and ventilation in the building. They are located at a height of 0.75–0.9 m from the floor level. The window area should be 15–20 per cent of the floor area. Another thumb rule used to determine the size and number of windows is that for every 30 m3 of inside volume, there should be 1 m² of window opening.
Ventilators are provided at or very close to roof/floor levels to provide good ventilation in the building. They are small windows but with fixed glass panes that permit ventilation. They may have hanging horizontal shutters that are operated with ropes.
Floors
Floors give useful working area to the occupants. The ground floor is prepared by filling brickbats, waste stones, gravel, etc., up to the plinth level, which is well compacted with a sand layer on top. Then a lean concrete course, 1:4:8, 100 mm thick, is laid. On this, a damp-proof course may be provided. Finally, floor finishing is done as per the requirement of the owner. The cheapest floor finish for an average house is done with 20–25 mm rich mortar course finished with red oxide. Superior houses are provided with mosaic or marble finishes.
Upper storey floors are mostly prepared with RCC these days. Earlier, jack arch or filler joist floors were used for upper storeys.
Roofs
The roof is the topmost portion, which provides a cover to the building. It should be leakproof. Sloping roofs like tiled and AC sheets give good leak cover though they do not allow the construction of additional floors. Tiled roofs also give good thermal protection.
Flat roofs allow the construction of additional floors in future. They also provide a terrace, which is an added benefit for the occupants. Water tanks can also be placed over flat roofs. The disadvantage of flat roofs is the difficulty in making it leak-proof.
Steps, Stairs, Lifts and Rooms
Steps give convenient access from ground level to ground floor level. They are required at doors in the outer wall. Sometimes, they are also required within a building when a floor is at a slightly different level. Steps ideally require a tread of 250–300 mm and a rise of 150 mm. The number of steps required depends on the difference in the levels to be negotiated. Stairs are a series of steps giving access from one floor to another floor. They should consist of steps of equal rise. In no case should the rise of two consecutive steps be different.
In case of buildings having height of more than 13 m, lift has to be provided. In all public buildings, lifts are to be provided, particularly for the convenience of old and disabled persons. In a hostel, G + 3 floors may be built without lifts, but in residential buildings, the maximum number of floors permitted without lift is only G + 2. The lift should be located near the entrance of the building. The size of the lift is decided by the expected number of users during peak hours. Lifts are available with a capacity of up to 20 persons.
Ramps are sloping floors built to connect floors at different levels. They are required for physically challenged persons who use wheelchairs.
Finishing
Ceilings, walls and floors need smooth finishing with plaster. They are then covered with whitewash, distemper, paint or tiles. The aim finishing work is to
- Give protective cover
- Improve aesthetic look
- Rectify defective workmanship
Finishing work for plinth consists of pointing, while for the floor, it consists of polishing.
Building Services
A number of essential service works are required in a building. These include water supply, sanitary connections, electric supply and construction of cupboards and showcases. For storing water from the municipal supply or from a tanker, a sump is built in the premises near the street. Water is pumped from the sump to overhead tanks placed on or above the roof level so as maintain a 24-hour water supply. Plumbing work is done so as to enable water supply in the kitchen, bathrooms, water closets, sinks and garden taps.
For draining rainwater from the roof, downtake pipes of at least 100 mm diameter should be used. Proper slope should be given on the roof towards the downtake pipes. These pipes should be fixed at 10–15 mm below the roof surface. The sanitary fittings are to be connected to stoneware pipes with suitable trays and chambers. Stoneware pipes are finally connected to underground drainages of municipal lines or to the septic tank.
Electric supply is another important building service. Wiring is done during the construction of the building. Sufficient points are provided for lights, fans and other electrical appliances. Switchboards are provided to receive electric supply from the public distribution system and distribute it to various parts of the building. A building also needs carpentry work. This includes cupboards, showcases, racks, and so on.
FAQs COVERED IN THIS POST
WHAT ARE THE BASIC COMPONENTS OF A BUILDING?
WHAT IS FOUNDATION OF THE BUILDING?
WHAT ARE WALLS AND COLUMNS OF A BUILDING?
WHAT IS THE FINISHING WORK OF A BUILDING?
WHAT ARE BUILDING SERVICES OF A BUILDING?
RELATED POSTS
CLASSIFICATION OF BUILDINGS BASED ON OCCUPANCY
CLASSIFICATION OF BUILDINGS BASED ON TYPE OF CONSTRUCTION
ALSO READ THE SURVEYING SUBJECT : SURVEYING - ALL TOPICS











Post a Comment