BASIC QUANTITIES AND RATIOS IN SOIL MECHANICS - POROSITY, VOID RATIO, DEGREE OF SATURATION, PERCENT AIR VOIDS, AIR CONTENT (StudyCivilEngg.com)
BASIC QUANTITIES AND RATIOS IN SOIL MECHANICS
SUBJECT : SOIL MECHANICS
A number of basic quantities or ratios defined below are useful in predicting the engineering behaviour of the soil. The general three-phase diagram for soil is quite helpful in understanding these basic quantities or ratios, and also in the development of more useful relationships between the various quantities. In a three-phase diagram it is conventional to represent volumes of the phases on the left side of the phase-diagram and their weights or masses on the right side as shown in below figures respectively. The total volume V of the soil mass is equal to the volume of air Va plus the volume of water Vw plus the volume of solid particles or soil grains Vs, i.e.,
V = (Va + Vw + Vs)
Also the volume of voids Vv is equal to the volume of air Va plus the volume of water Vw, i.e.,
Vv = (Va + Vw)
and hence
V = Vv + Vs
Similarly the total weight W of the soil mass is equal to the weight of air Wa plus the weight of water Ww plus the weight of solid particles or soil grains Ws, i.e.,
W = (Wa + Ww + Ws)
The weight Wv of the materials occupying the voids is equal to the weight of air Wa plus the weight of water Ww, i.e.,
Wv = Wa + Ww
However, the weight of air being negligible, Wa ∼ 0, and hence
Wv = Ww and the total weight of the soil mass is W = (Ww + Ws)
If instead of weight, mass is considered then the total mass M of the soil mass is equal to the mass of air Ma plus the mass of water Mw plus the mass of solid particles or soil grains
Ms, i.e., M = (Ma + Mw + Ms)
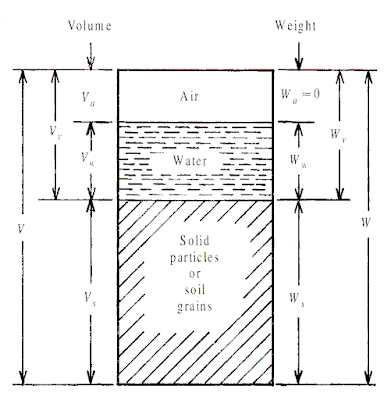 |
| Three Phase Diagram of soil showing Volume and Weight |
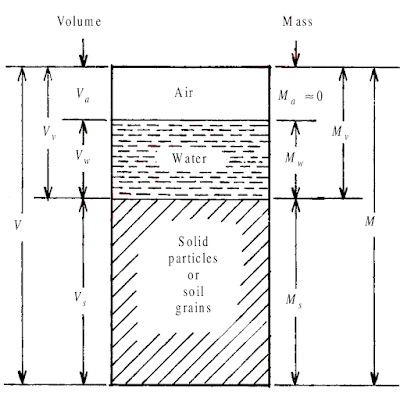 |
| Three Phase Diagram of soil showing Volume and Mass |
The mass Mv of the materials occupying the voids is equal to the mass of air Ma plus the mass of water Mw, i.e., Mv = (Ma + Mw). Again the mass of air being negligible, Ma ∼ 0, and hence Mv = Mw and the total mass of the soil mass is M = Mw + Ms
POROSITY
What is Porosity?
Porosity of a soil mass is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids Vv to the total volume of the soil mass V. It is denoted by symbol n. Thus
n = Vv/V --- Equation 1
Porosity is commonly expressed as a percentage. Thus
n = Vv/V × 100 --- Equation 2
It is also referred to as percentage voids
VOID RATIO
What is Void Ratio?
Void ratio of a soil mass is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids Vv to the volume of solids or solid particles Vs in the soil mass. It is denoted by symbol e and is generally expressed as a decimal fraction. Thus,
e = Vv/Vs --- Equation 3
Both porosity and void ratio are the measures of denseness (or looseness) of soils. As the soil becomes more and more dense the values of both porosity and void ratio decrease. The term porosity is more commonly used in other fields of engineering such as agricultural engineering. In soil mechanics void ratio is used more than porosity to characterise the natural state of soil. This is so because in void ratio the denominator Vs, the volume of solids remains more or less constant under the application of pressure, and only the numerator Vv, the volume of voids changes, but in the case of porosity, both the numerator Vv, the volume of voids and the denominator V, the total volume of the soil mass change under the application of pressure.
DEGREE OF SATURATION
What is Degree of Saturation?
Degree of saturation of a soil mass is defined as the ratio of the volume of water Vw present in the voids to the volume of voids Vv. It is denoted by symbol S (or Sr). Thus
S (or Sr) = Vw/Vv ---Equation 4
Degree of saturation is commonly expressed as a percentage. Thus
S (or Sr) = Vw/Vv x 100 --- Equation 5
It is also known as percent saturation. For a fully saturated soil mass Vw=Vv, and hence S (or Sr) = 1 or 100%. For a perfectly dry soil Vw = 0, and hence S (or Sr) = 0. In both these conditions the soil mass is considered to be a two-phase system. When the degree of saturation of a soil is between zero and 100%, the soil mass is said to be ‘partially’ saturated which is the most common condition found in nature, and in this condition the soil mass is considered to be a three-phase system.
PERCENT AIR VOIDS
Percent air voids of a soil mass is defined as the ratio of the volume of air Va present in the voids to the total volume of the soil mass V. It is denoted by symbol na. Thus
na = Va/V --- Equation 5
Percent air voids is commonly expressed as percentage. Thus
na = Va/V × 100
AIR CONTENT
Air content of a soil mass is defined as the ratio of the volume of air Va present in the voids to the total volume of voids Vv. It is denoted by symbol ac. Thus
ac = Va/Vv
Air content is commonly expressed as a percentage. Thus ac = Va/Vv × 100
FAQs COVERED IN THIS POST
What is Porosity?
What is Degree of Saturation?
What is Percent Air Voids?
What is Air Content?
What are the basic quantities in Soil Mechanics?
What are the basic ratios in Soil Mechanics?
What are the basic ratios in Soil Mechanics?
RELATED POSTS
- RESIDUAL AND TRANSPORTED SOILS
- COMPOSITION OF SOILS
- INTRODUCTION & BASIC DEFINITIONS IN SOIL MECHANICS
- SOIL GROUPS IN INDIA
- FORMATION OF SOILS
- DIFFERENT TYPES OF SOILS
ALSO READ
- SURVEYING - STUDY ONLINE
- BUILDING MATERIALS AND CONSTRUCTION - STUDY ONLINE
- FLUID MECHANICS - STUDY ONLINE





Post a Comment